Minotaur C
NOTE: AIAA only page editing

Falcon 9 Launch

Falcon Heavy Launch
About Northrop Grumman Space Systems
Northrop Grumman is a pioneering company. We design, develop, build and support some of the world’s most advanced products, from cutting-edge aircraft and next-generation spacecraft to unrivaled cyber security systems and all-seeing radars.
Atlas Vehicle Descriptions
Minotuar C
General Description
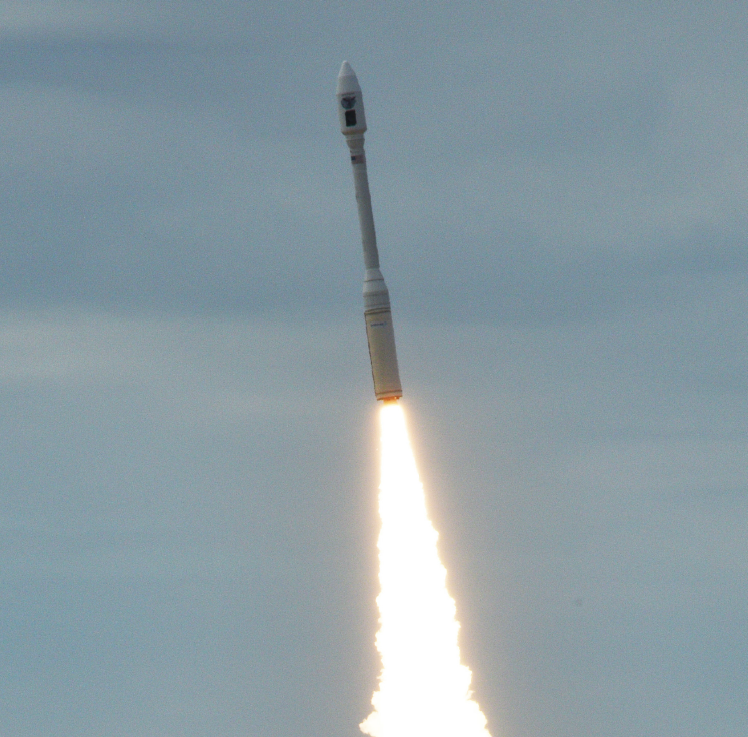

Northrop Grumman Minotaur-C launches from Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg AFB, carrying 10 small satellites owned by Planet Labs, October 31, 2017.
National Origin
United StatesMain Organization
Summary
Flight Rate
Estimated Launch Price
$40-50 million (OSC, 2014)
Spaceports
| Launch Site | Cape Canaveral AFS, Florida |
| Location | 28.5°N, 81.0°W |
| Available Inclinations | 28.5–51 deg |
Primary Missions
Small LEO and SSO payloads
Status
Key Organizations
Marketing Organization
Launch Service Provider
Prime Contractor
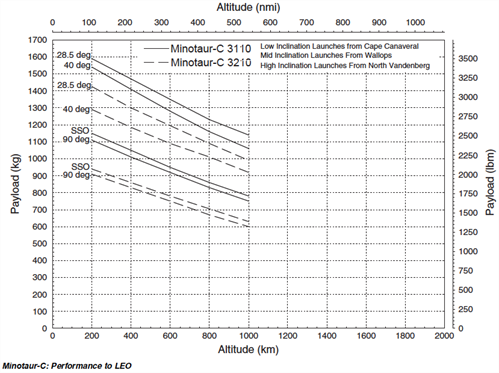
Performance
| 200 km (108 nmi), 28.5 deg | 14578 kg (3214 lbm) |
| 200 km (108 nmi), 90 deg | |
| Space Station Orbit: 407 km (220 nm), 51.6 deg | ? |
| Sun-Synchronous Orbit: 800 km (432 nm), 98.6 deg | 1054 kg (2324 lbm) |
| GTO: 185×35,786 km (100×19,323 nm), 28.5 deg | |
| GEO | No capability |
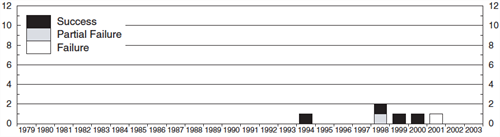
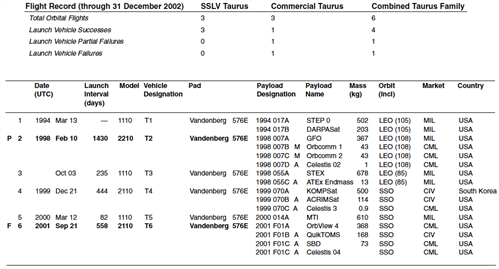
Flight Record (through 30 June 2021)
| Total Orbital Flights | 10 |
| Launch Vehicle Successes | 7 |
| Launch Vehicle Partial Failures | 0 |
| Launch Vehicle Failures | 3 |
Orbital Flights Per Year
| Failure Descriptions: | |||
| P | 1998 Feb 10 T2 | 1998 007 | Delivery orbit apogee was 91 km higher than planned. Although considered a partial failure according the definition used in this publication, both Orbital Sciences and the payload customer consider the launch a success. |
| F ADD: Minotaur-C 2004-2021 failures and partial failures (spreadsheet) here (once available) |
2001 Sep 21 T6 | 2001 F01 | When the second stage ignited at T+83 seconds, a nozzle gimbal actuator drive shaft siezed for approximately 5 seconds causing loss of control. The vehicle recovered and continued to fly the mission profile, but failed to reach a stable orbit and reentered near Madagascar. |